spring AOP 切面编程(概念+原理+实现方式) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › spring aop切点切面 › spring AOP 切面编程(概念+原理+实现方式) |
spring AOP 切面编程(概念+原理+实现方式)
|
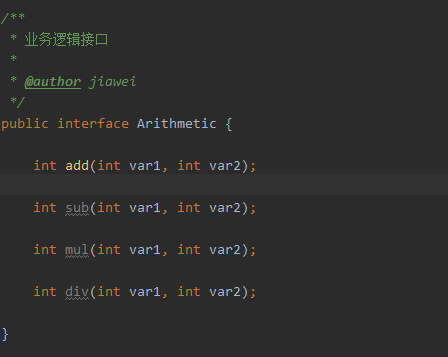
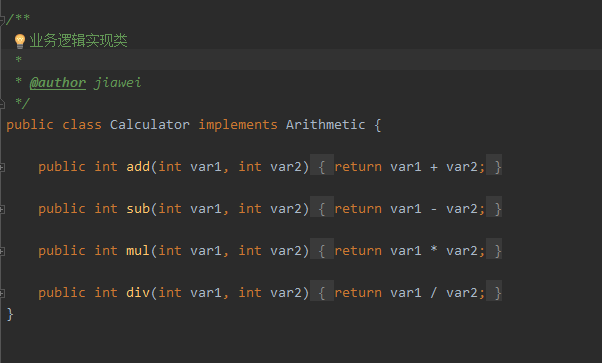
一、什么是AOP AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),即面向切面编程,可以说是OOP(Object Oriented Programming,面向对象编程)的补充和完善。OOP引入封装、继承、多态等概念来建立一种对象层次结构,用于模拟公共行为的一个集合。不过OOP允许开发者定义纵向的关系,但并不适合定义横向的关系,例如日志功能。日志代码往往横向地散布在所有对象层次中,而与它对应的对象的核心功能毫无关系对于其他类型的代码,如安全性、异常处理和透明的持续性也都是如此,这种散布在各处的无关的代码被称为横切(cross cutting),在OOP设计中,它导致了大量代码的重复,而不利于各个模块的重用。 AOP技术恰恰相反,它利用一种称为"横切"的技术,剖解开封装的对象内部,并将那些影响了多个类的公共行为封装到一个可重用模块,并将其命名为"Aspect",即切面。所谓"切面",简单说就是那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的逻辑或责任封装起来,便于减少系统的重复代码,降低模块之间的耦合度,并有利于未来的可操作性和可维护性。 使用"横切"技术,AOP把软件系统分为两个部分:核心关注点和横切关注点。业务处理的主要流程是核心关注点,与之关系不大的部分是横切关注点。横切关注点的一个特点是,他们经常发生在核心关注点的多处,而各处基本相似,比如权限认证、日志、事物。AOP的作用在于分离系统中的各种关注点,将核心关注点和横切关注点分离开来。 二、AOP核心概念 1、横切关注点 对哪些方法进行拦截,拦截后怎么处理,这些关注点称之为横切关注点 2、切面(aspect) 类是对物体特征的抽象,切面就是对横切关注点的抽象 3、连接点(joinpoint) 被拦截到的点,因为Spring只支持方法类型的连接点,所以在Spring中连接点指的就是被拦截到的方法,实际上连接点还可以是字段或者构造器 4、切入点(pointcut) 对连接点进行拦截的定义 5、通知(advice) 所谓通知指的就是指拦截到连接点之后要执行的代码,通知分为前置、后置、异常、最终、环绕通知五类 6、目标对象 代理的目标对象 7、织入(weave) 将切面应用到目标对象并导致代理对象创建的过程 8、引入(introduction) 在不修改代码的前提下,引入可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或字段 三、AOP的三种实现 1、基于xml配置方式 ①创建业务逻辑接口以及其具体实现类
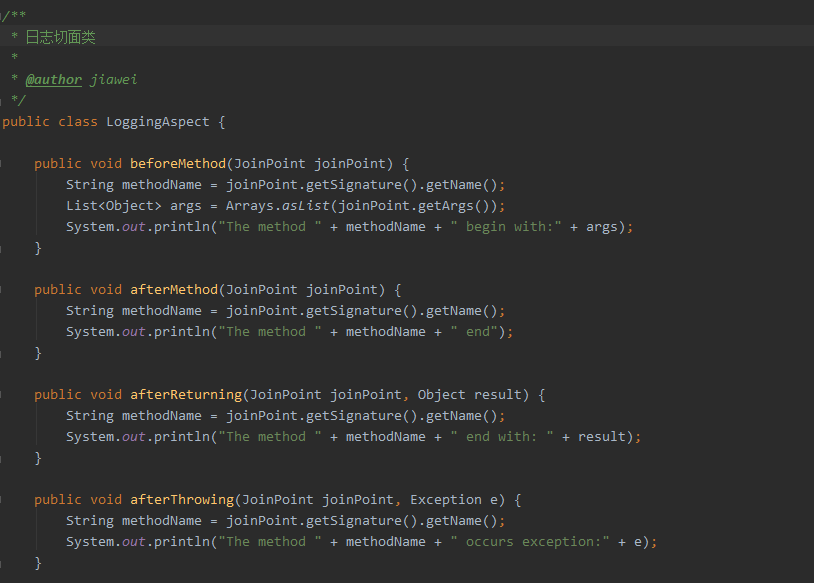
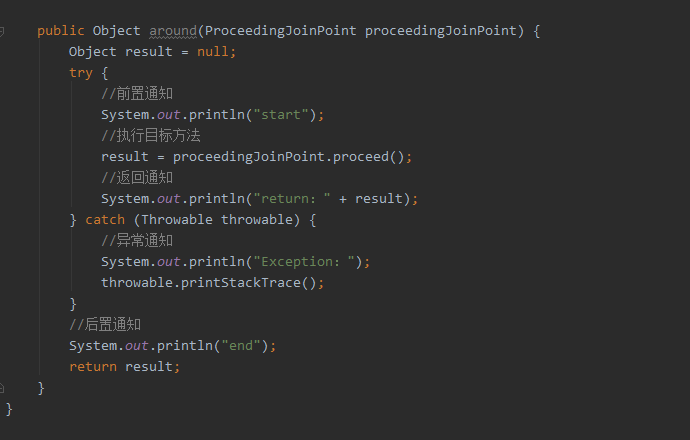
②创建切面类
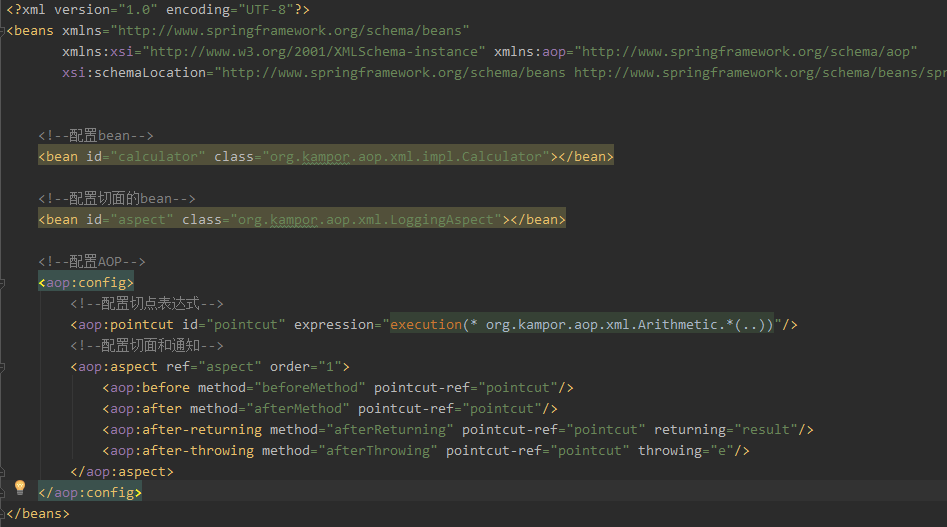
③详细的xml配置信息,首先将业务逻辑类和切面类加入IOC中
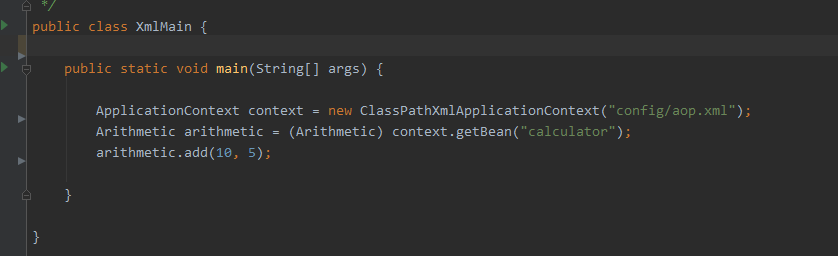
④xml配置AOP测试
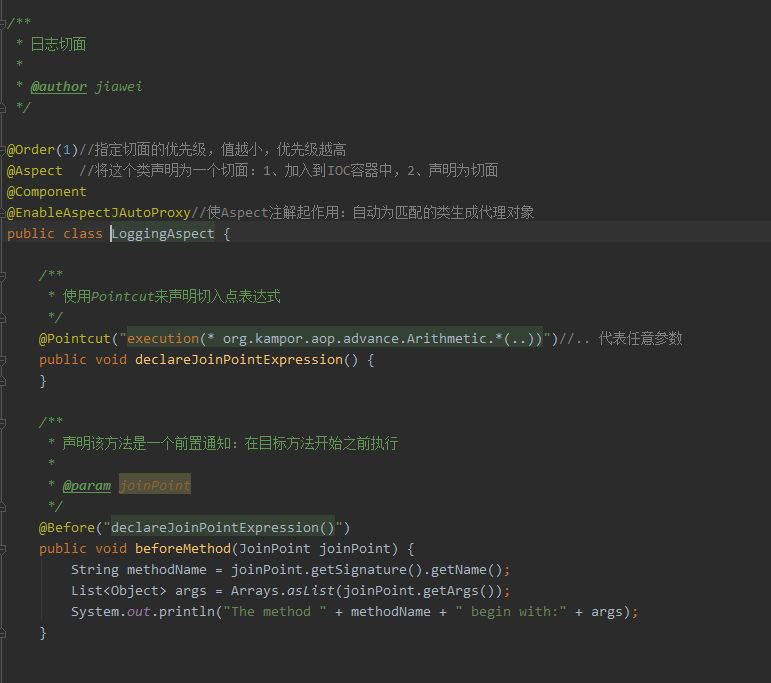
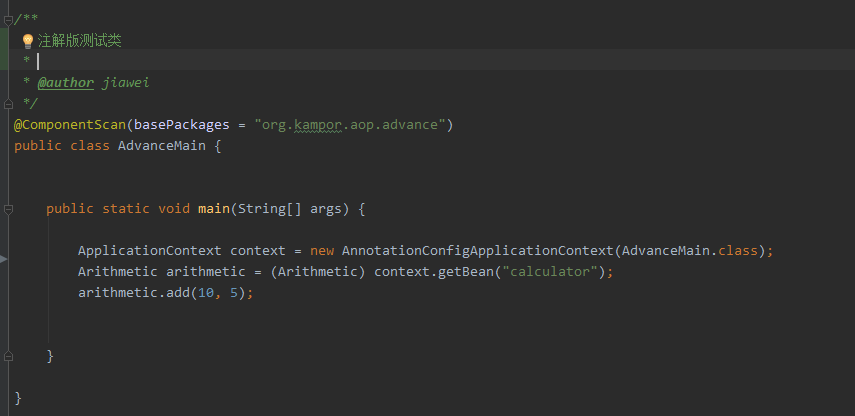
2、Spring纯注解配置aop 首先和上面一样创建业务逻辑接口和实现类,然后再切面类添加对应注解,注意@EnableAspectJAutoProxy的使用,不能忘记。
测试类,扫描组件
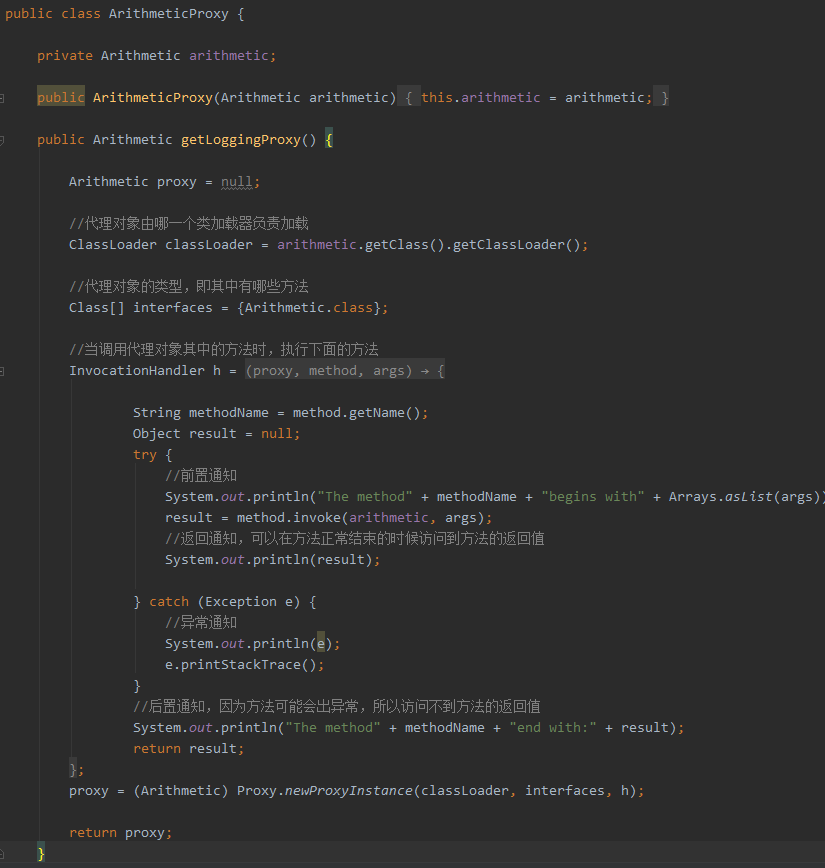
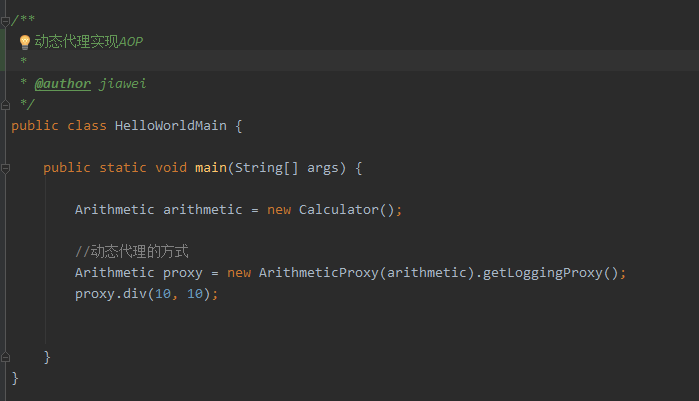
3、动态代理的方式实现AOP
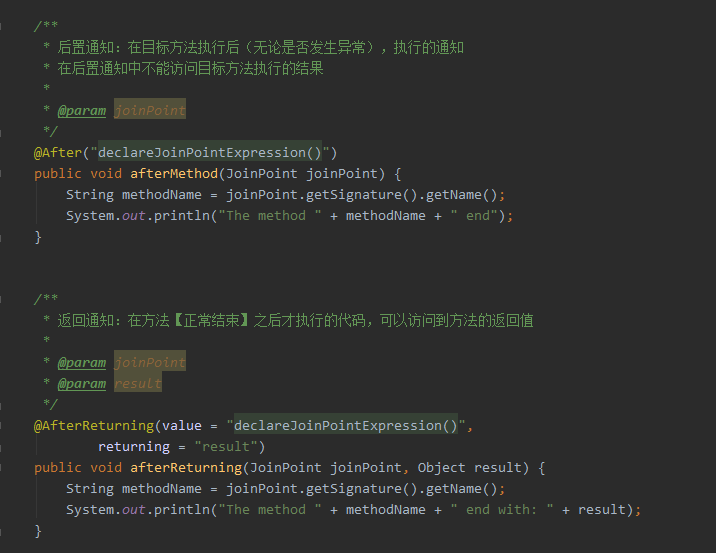
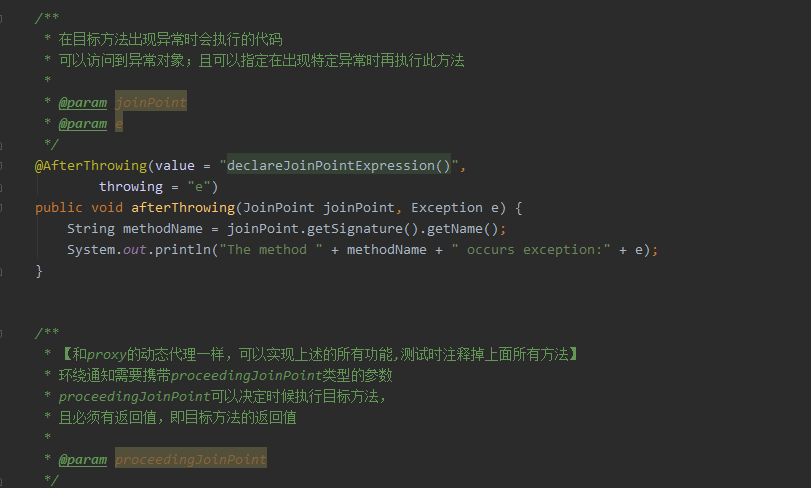
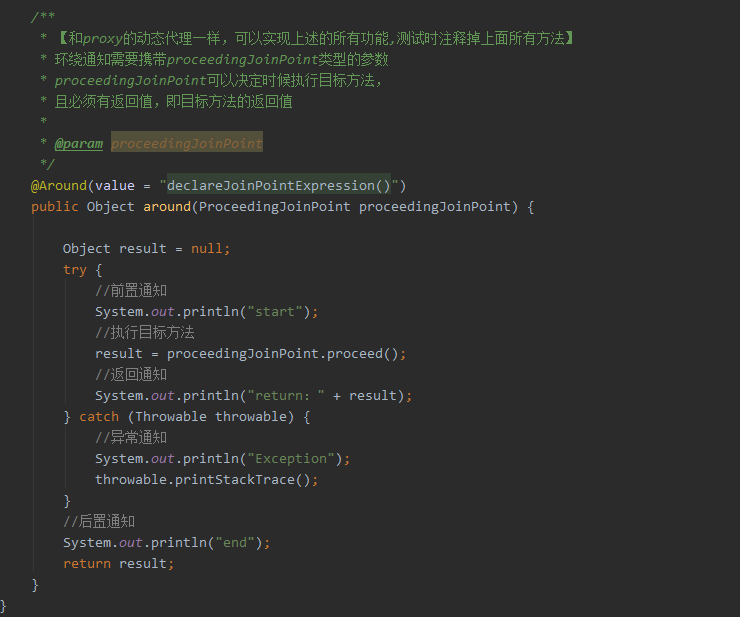
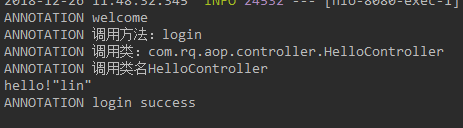
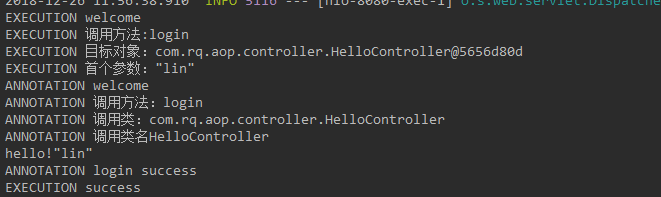
springAOP增强处理 @Around的作用 既可以在目标方法之前织入增强动作,也可以在执行目标方法之后织入增强动作; 可以决定目标方法在什么时候执行,如何执行,甚至可以完全阻止目标目标方法的执行; 可以改变执行目标方法的参数值,也可以改变执行目标方法之后的返回值; 当需要改变目标方法的返回值时,只能使用Around方法; 虽然Around功能强大,但通常需要在线程安全的环境下使用。因此,如果使用普通的Before、AfterReturing增强方法就可以解决的事情,就没有必要使用Around增强处理了。注解方式:如果需要对某一方法进行增强,只需要在相应的方法上添加上自定义注解即可 package com.rq.aop.common.advice; import com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect //标注增强处理类(切面类) @Component //交由Spring容器管理 public class AnnotationAspect { /* 可自定义切点位置,针对不同切点,方法上的@Around()可以这样写ex:@Around(value = "methodPointcut() && args(..)") @Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation)") public void methodPointcut(){} @Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation2)") public void methodPointcut2(){} */ //定义增强,pointcut连接点使用@annotation(xxx)进行定义 @Around(value = "@annotation(around)") //around 与 下面参数名around对应 public void processAuthority(ProceedingJoinPoint point,MyAnnotation around) throws Throwable{ System.out.println("ANNOTATION welcome"); System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用方法:"+ around.methodName()); System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类:" + point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName()); System.out.println("ANNOTATION 调用类名" + point.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName()); point.proceed(); //调用目标方法 System.out.println("ANNOTATION login success"); } }注解类 package com.rq.aop.common.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行时有效 @Target(ElementType.METHOD)//作用于方法 public @interface MyAnnotation { String methodName () default ""; }Controller package com.rq.aop.controller; import com.rq.aop.common.annotation.MyAnnotation; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller @RequestMapping("/hello") public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/login/{name}") @MyAnnotation(methodName = "login") public void login(@PathVariable String name){ System.out.println("hello!"+name); } }运行结果: 匹配方法执行连接点方式 package com.rq.aop.common.advice; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component @Order(0) //设置优先级,值越低优先级越高 public class ExecutionAspect { @Around(value = "execution(* com.rq.aop.controller..*.*(..))") public void processAuthority (ProceedingJoinPoint point)throws Throwable{ System.out.println("EXECUTION welcome"); System.out.println("EXECUTION 调用方法:" + point.getSignature().getName()); System.out.println("EXECUTION 目标对象:" + point.getTarget()); System.out.println("EXECUTION 首个参数:" + point.getArgs()[0]); point.proceed(); System.out.println("EXECUTION success"); } }eg. 任意公共方法的执行:execution(public * *(..)) 任何一个以“set”开始的方法的执行:execution(* set*(..)) AccountService 接口的任意方法的执行:execution(* com.xyz.service.AccountService.*(..)) 定义在service包里的任意方法的执行: execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..)) 定义在service包和所有子包里的任意类的任意方法的执行:execution(* com.xyz.service..*.*(..))第一个表示匹配任意的方法返回值, …(两个点)表示零个或多个,第一个…表示service包及其子包,第二个表示所有类, 第三个*表示所有方法,第二个…表示方法的任意参数个数 定义在pointcutexp包和所有子包里的JoinPointObjP2类的任意方法的执行:execution(*com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp..JoinPointObjP2.*(..))") pointcutexp包里的任意类: within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.*) pointcutexp包和所有子包里的任意类:within(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp..*) 实现了Intf接口的所有类,如果Intf不是接口,限定Intf单个类:this(com.test.spring.aop.pointcutexp.Intf) 当一个实现了接口的类被AOP的时候,用getBean方法必须cast为接口类型,不能为该类的类型 带有@Transactional标注的所有类的任意方法: @within(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) @target(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) 带有@Transactional标注的任意方法: @annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) @within和@target针对类的注解,@annotation是针对方法的注解 参数带有@Transactional标注的方法:@args(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) 参数为String类型(运行是决定)的方法: args(String) 运行结果:
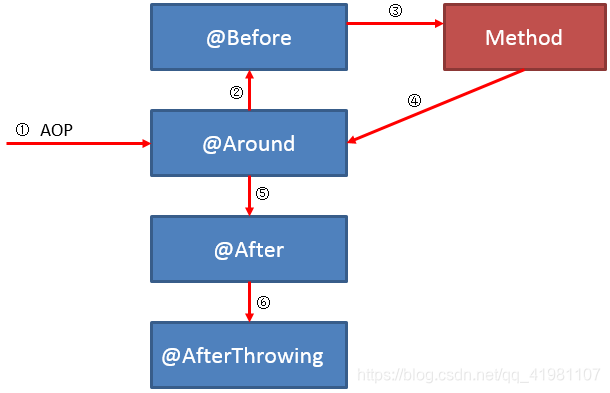
切面执行顺序: |
【本文地址】
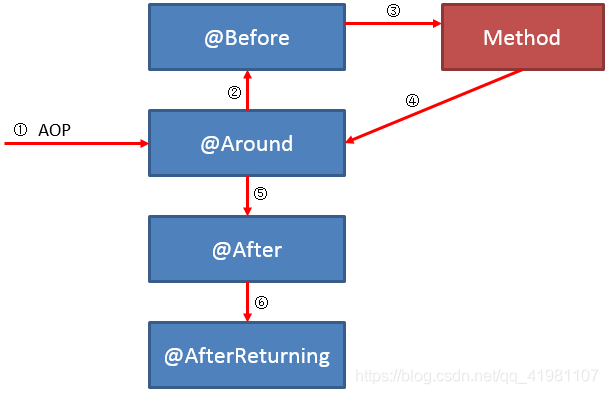 异常:
异常: